Panoramic X-Rays and CT Scans: Guide to Benefits, Uses, and Key Role in Successful Implants, Orthodontics, and Surgery.
Panoramic and CT Scans: The Comprehensive Guide to 3D Imaging and Accurate Diagnosis in Dentistry
Section 1: Introduction: The Importance of Advanced Radiological Imaging in Dentistry
Oral and dental health is an essential part of overall health, and achieving a successful and lasting treatment plan relies heavily on accurate diagnosis. What the naked eye sees is not enough; most deep-seated root and bone issues are hidden in concealed areas that only technological advancements in radiology can reveal.
Panoramic X-rays and Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) represent the most vital and modern tools in advanced dental clinics. These technologies provide a deep, comprehensive view of the jaws, teeth, bones, and surrounding tissues, converting guesswork into certainty and ensuring treatment procedures are carried out with maximum efficiency and minimal risk.
This comprehensive guide is designed to cover every angle related to these two technologies, clarifying the difference between panoramic and CT scans, when each is needed, and how they contribute to the success of treatments like dental implants and orthodontics, all the way to the safety measures adopted by leading centers.
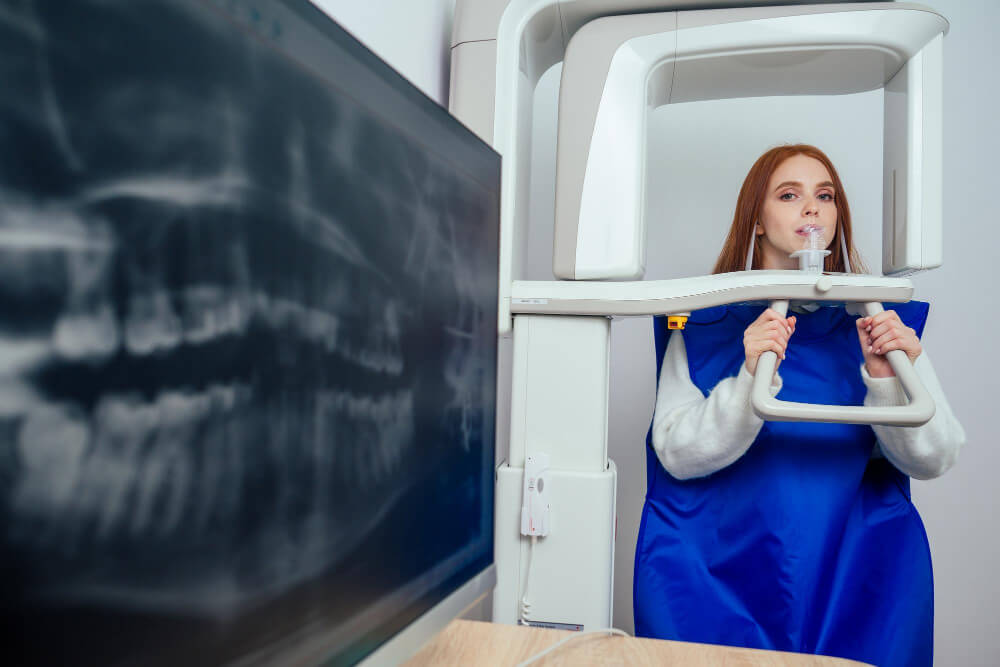

Section 2: What is a Panoramic X-ray? A Comprehensive Two-Dimensional View
The Panoramic X-ray is a very common radiological imaging technique, providing a wide, panoramic shot that displays the entire region of the mouth, jaws, and teeth in a single two-dimensional (2D) image.
How the Panoramic X-ray Device Works
The device operates through a rotational movement, where the X-ray tube source and the sensor rotate around the patient’s head, producing a flat, comprehensive image. This type of X-ray does not require inserting any imaging device inside the mouth, making it comfortable and fast.
Anatomical Structures Shown by Panoramic X-rays
Although a 2D image, it provides crucial information that cannot be obtained from small, traditional dental X-rays. It enables the dentist to see the following:
All Teeth: Including teeth that have not yet erupted or impacted molars.
The Mandible and Maxilla: A general assessment of the skeletal structure.
The Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ): A quick evaluation of the condition of the joint connecting the jaw to the skull.
The Maxillary Sinuses: Especially the sinuses close to the roots of the posterior teeth.
Section 3: The 6 Main Diagnostic Uses of Panoramic X-rays
Panoramic X-rays are critically important for initial diagnosis and general treatment planning. Their key uses include:
Diagnosing and Locating Impacted Wisdom Teeth: They accurately show the impaction angle of the wisdom tooth and help estimate its proximity to the mandibular nerve canal, which is vital before surgical extraction.
Evaluating Gum Diseases and Bone Level: They enable the doctor to measure the supporting bone level around the teeth, detecting any bone loss resulting from periodontal diseases (advanced gum inflammation).
Detecting Jaw Tumors and Cysts: They are used as a primary screening tool to detect any abnormal growth (such as cysts or tumors) in the jawbones.
Planning Orthodontic Treatments: They provide a comprehensive image of the position of all teeth and the relationship between the jaws before beginning orthodontic treatment.
Evaluating Trauma and Injury Effects: Detecting major fractures in the jawbones resulting from accidents or injuries.
Diagnosing Congenital Abnormalities and Metabolic Bone Diseases: They help reveal early signs of jaw deformities, such as cleft lip or cleft palate, which may require multidisciplinary surgical intervention. They can also reveal indicators of general bone diseases affecting jawbone density, which necessitates referring the patient to a specialist in metabolic bone diseases before starting any dental procedure.
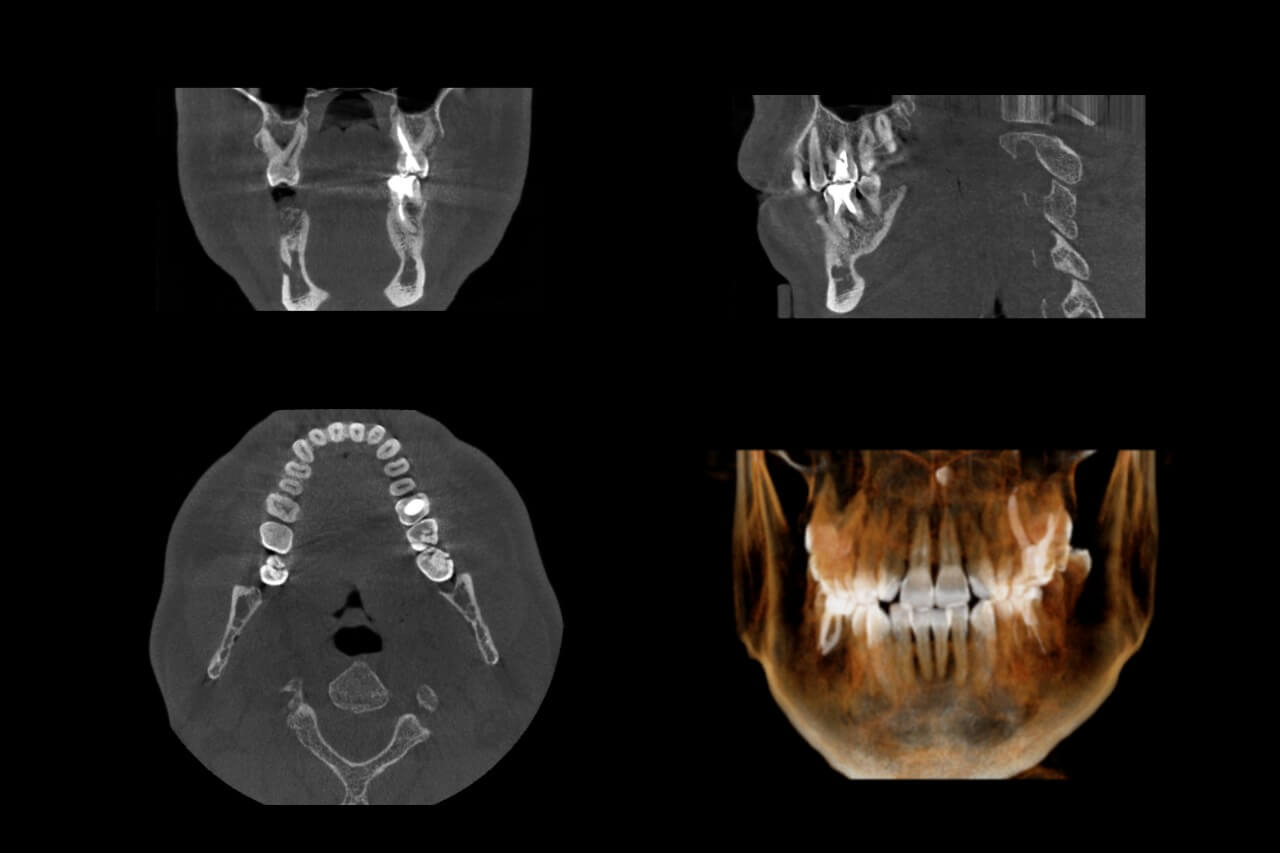
Section 4: Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT): A Qualitative Leap in Diagnosis (Explanation and Deep Dive)
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), also known as 3D imaging, is a true revolution in dental diagnosis, having moved practitioners from relative guesswork to absolute certainty in treatment planning.
The Core Concept: From Two Dimensions to Three Dimensions
In traditional (panoramic) X-rays, complex 3D structures (like teeth and bone) are compressed into a flat 2D image. This compression inevitably leads to Superimposition of structures, where near and far objects overlap, obscuring vital details.
In contrast, the CBCT technology uses a cone-shaped X-ray beam that rotates around the patient’s head, capturing hundreds of images from various angles in mere seconds. Advanced computer software then collects and reconstructs these images to create a digital Three-Dimensional (3D Model) of the jaws.
Technical Features Driving the Qualitative Leap
The CBCT’s qualitative leap lies in its ability to provide three diagnostic pieces of information that were not previously available with the same accuracy:
True Measurements (1:1 Accuracy): CBCT provides highly accurate measurements at a 1:1 ratio, meaning the measurements taken from the screen are the true dimensions in the patient’s mouth. This completely eliminates the Magnification issue inherent in panoramic X-rays, making it the only reliable tool for surgical planning.
Axial and Cross-Sectional Views: CBCT allows the doctor to virtually slice the jaw in any plane (sagittal, coronal, axial). The doctor can view the bone and teeth from the front, side, or even from above (axial view), which reveals the bone width with unprecedented accuracy.
Determining Bone Density and Quality: CBCT does not stop at measuring bone dimensions; it can determine bone density (using Hounsfield Units), which helps in selecting the appropriate implant type for the highest success rates in osseointegration.
4. The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Software in Data Analysis (AI-Driven Analysis)
To complete the diagnostic accuracy and reach its highest levels, advanced analysis software must utilize the immense 3D data provided by CBCT. Leading centers do not just produce raw CBCT images; they use specialized software (often relying on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning algorithms) to perform the following digital analyses:
Automatic Identification of Vital Structures: Mandibular nerve pathways (like the inferior canal) and blood vessels are instantly and automatically identified.
Automatic Segmentation: Separating teeth, roots, and bone from soft tissues in the 3D model to facilitate measurements.
Treatment Simulation: Using the software to simulate the placement of implants or the movement of teeth (in orthodontics) before the actual treatment begins.
This integration of 3D imaging and computer analysis ensures that the human diagnosis, supported by the expertise of Dr. Mohamed Omara, is backed by the latest digital analysis tools to minimize the margin of error to zero and provide the foundation for digital surgical guide fabrication.
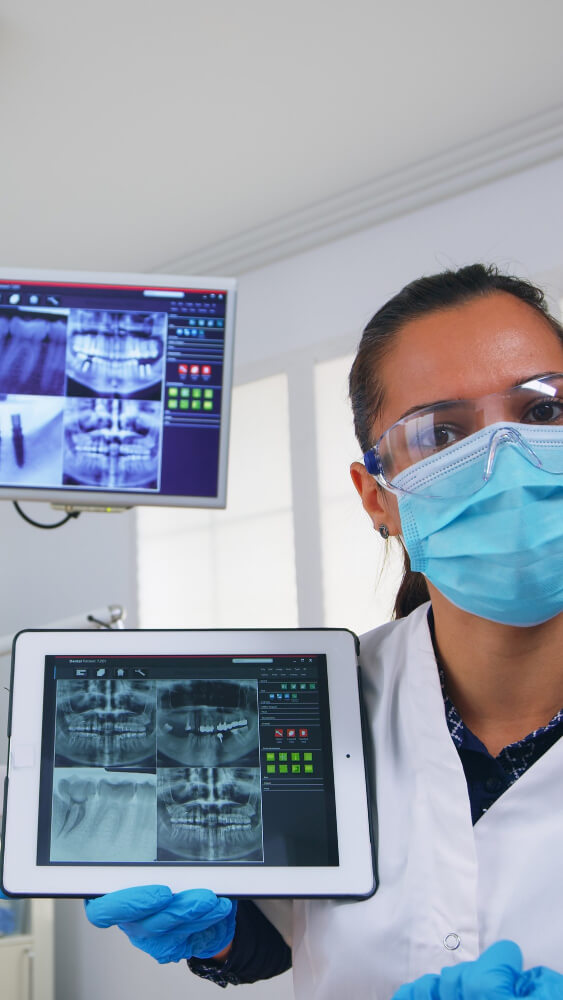

Section 5: Vital Applications of CBCT in Treatment Planning
CBCT is indispensable in cases requiring extreme precision and calculated treatment planning. Its most important vital applications are focused on the following:
1. Its Decisive Role in Dental Implant Planning
In the field of dental implants, CBCT is the gold standard. It enables the doctor to:
Accurately Measure Bone Density, Height, and Width: This information is essential for determining the appropriate size and exact location of the implant.
Identify Nerve Pathways and Avoid Injury: CBCT accurately shows the location of the mandibular nerve canal or the maxillary sinuses, allowing the doctor to determine a safe distance for implant placement and prevent nerve damage.
Designing the Surgical Guide: The 3D image is used to design a precise template (Surgical Guide) used during surgery to ensure the implant is placed in the ideal position.
2. Advanced Diagnostic and Surgical Applications
Diagnosing Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders: Evaluating bone changes in the joint (such as erosion or dislocation).
Treating Complex Root Canals (Endodontics): Detecting additional canals, root fractures, or hidden infections that are difficult to see on regular X-rays.
Evaluating Complex Orthodontic Cases: Accurately determining the position of impacted teeth for correct traction.
Differentiating True Tumors from Cysts: CBCT provides the ability to determine the density of the mass, the shape of its borders, and the extent of bone erosion around it, which is necessary for differential diagnosis. This accuracy allows the surgeon to plan the surgical excision within a safe margin, minimizing potential disease spread.
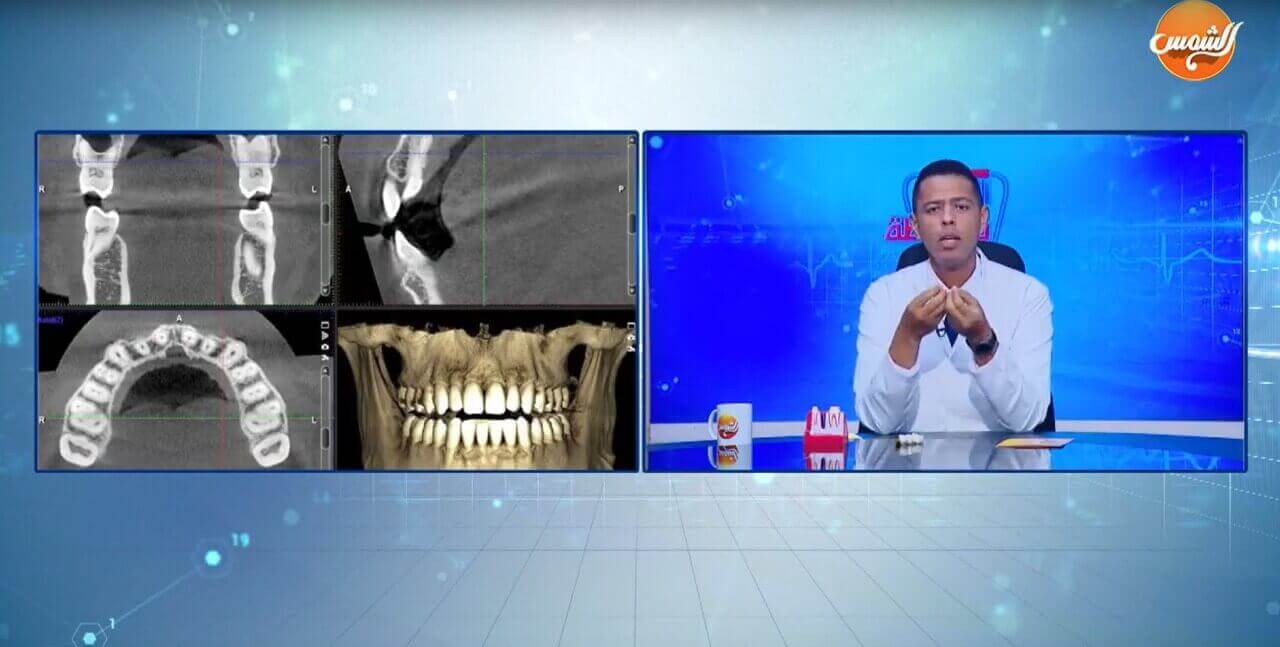
Section 6: Comprehensive Comparison: Panoramic vs. CBCT Scans (Accuracy and Measurements)
The choice between the two techniques depends on the diagnostic goal. The comparison between Panoramic and CT scans goes beyond mere visualization, extending to their direct impact on the accuracy of clinical measurements and the treatment plan:
| Feature | Panoramic X-rays (2D) | CBCT Scans (3D) |
| Measurement Accuracy | Moderate to Low (Suffers from Magnification distortion) | Very High (True 1:1 measurements without distortion) |
| Imaging | Two-Dimensional (Flat view of the jaws) | Three-Dimensional (Volumetric view from all angles) |
| Common Use | Routine checkups, wisdom teeth, initial orthodontic planning. | Dental Implants, jaw surgery, complex root canal treatment. |
Distortion vs. Absolute Accuracy:
Panoramic X-rays (2D): Suffer from the phenomenon of Magnification (distortion), meaning measurements taken directly from the image may contain a margin of error up to 30%. This margin is unacceptable for precision procedures.
CBCT Scans (3D): Provide true and accurate 1:1 measurements, eliminating any doubt in determining the implant length, diameter, and distance from vital structures. This absolute accuracy ensures complete safety during surgery.
Section 7: Radiation Exposure and Safety: Protection Measures in Leading Centers (Comprehensive Deep Dive)
One of the most common concerns for patients is radiation exposure. The reality is that modern dentistry relies on advanced digital devices specifically designed to reduce the radiation dose to the lowest possible level, with advanced centers adhering to extreme safety standards that exceed local requirements.
1. The “ALARA” Principle
All radiation safety protocols revolve around the “ALARA” principle, an acronym for “As Low As Reasonably Achievable.” This principle mandates that the doctor and clinics take an X-ray only when medically necessary, using the lowest possible radiation dose to achieve the required diagnostic purpose. This is the core of safe diagnosis.
2. Comparing Radiation Doses (Quantifying Exposure)
To alleviate anxiety, it is essential to contextualize the dental X-ray dose with daily exposure:
Panoramic X-rays: Equivalent to about 0.005 millisieverts (mSv), which is less than the dose a person naturally receives from the environmental background daily.
CBCT Scans: Typically range from 0.01 to 0.1 mSv, which is slightly higher than panoramic, but still a fraction of the dose the body absorbs during a long flight (which can reach 0.04 mSv) or the dose the body naturally receives from the environment over three days.
3. The Role of Technology in Risk Reduction
Digital Systems: Modern digital sensor technologies require less exposure time compared to old traditional X-ray films, reducing the dose by up to 80%.
Cone Beam Technology: The CBCT device emits a narrow cone-shaped X-ray beam that focuses only on the mouth and jaw area, instead of the broad fan beams used in traditional medical CT scanners. This focus drastically reduces scattered radiation to sensitive surrounding tissues of the head and neck.
4. Physical Protection Measures
Leading centers are committed to implementing additional physical protection barriers:
Lead Aprons: The patient must be provided with a thick, appropriate lead apron to cover the chest, abdomen, and reproductive organs, protecting rapidly dividing tissues from any scattered radiation.
Thyroid Collar: The thyroid gland is one of the most radiation-sensitive organs, and a special collar must be used to protect it, especially for children and women.
5. Dr. Mohamed Omara Center’s Commitment to International Quality Standards
To ensure the highest levels of safety for the patient and staff, adherence to international standards is crucial. The center’s certification with the International Quality Certificate (ISO) means:
Strict implementation of safe operating protocols.
Regular and continuous calibration of radiological devices to ensure the emitted radiation dose is the lowest effective dose.
Section 8: The Role of X-rays in the Success of Implant, Orthodontic, and Oral Surgery Treatment Plans (Comprehensive Deep Dive)
Panoramic and CT scans serve as the roadmap for the surgeon and dentist, being the differentiating factor that ensures the transition from trial-and-error treatment to precise computer-guided planning in complex procedures.
1. Inevitable Success in Implantology
Determining Bone Quality and Density: CBCT is the only tool that can measure Bone Density (using Hounsfield Units) at the intended implant site. This is vital for selecting the right implant and determining if the patient needs preparatory procedures like Bone Grafting before placement. This preemptive planning significantly lowers implant failure rates.
Guided Surgery: CBCT images are used to create a virtual model of the jaw. The doctor places the implants on the computer model, and then a Surgical Stent (Guide) is fabricated to direct the surgeon’s hand to place the implant at the ideal angle and depth. This technique ensures accuracy down to a fraction of a millimeter, making the procedure faster, safer, and less painful.
2. Precision in Orthodontic Planning
3D Cephalometric Analysis: While traditional panoramic X-rays (2D) are used for cephalometric analysis, CBCT allows for a 3D cephalometric analysis. This enables the orthodontist to understand the complex relationship between the teeth, jaws, and the base of the skull, which reduces the likelihood of relapse after treatment completion.
Impacted Teeth: For a successful treatment plan to bring an impacted tooth into the arch, its exact location, its relationship to adjacent tooth roots, and nerves must be known to the millimeter. CBCT provides a 3D view that precisely defines this position, minimizing the risks of damaging adjacent roots during the orthodontic traction process.
3. Safety in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Avoiding Vital Structures: In wisdom tooth extractions or cyst/tumor removal, CBCT accurately determines the distance between the surgical site and the Mandibular Nerve Canal or the maxillary sinus. This reduces the risk of serious complications, such as temporary or permanent numbness in the lower lip.
Sinus Lift: CBCT is used to accurately assess the thickness of the Schneiderian Membrane lining the maxillary sinus before a sinus lift procedure, minimizing the risk of membrane tearing and increasing the success of bone grafting.
Evaluating Fractures and Trauma: CBCT provides the optimal 3D evaluation for jaw and facial fractures, which cannot be achieved with conventional panoramic X-rays, facilitating the planning of fracture fixation surgery with the highest accuracy.
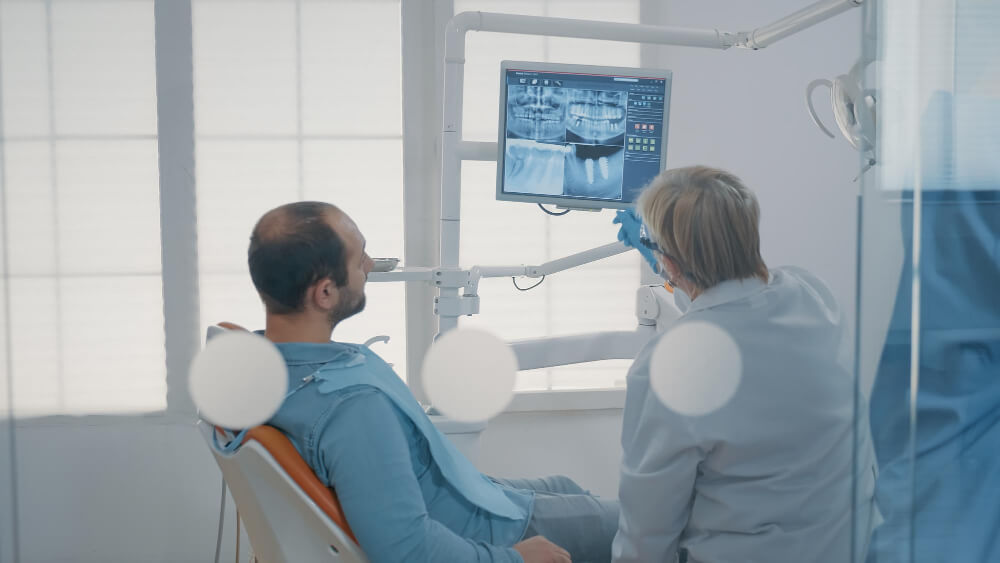
Section 9: The Doctor's Expertise and Authority in Reading X-rays and Accurate Diagnosis
Owning the latest equipment is not enough; the X-ray is merely a tool. The real power lies in the specialized doctor’s expertise in accurately reading and interpreting these complex images, and connecting them with the patient’s clinical examination.
The Impact of European Expertise on Diagnosis
Dr. Mohamed Omara, holding a Master’s Degree in Orthodontics and Cosmetic Dentistry from the University of Parma, Italy, applies a rigorous European diagnostic methodology that relies heavily on reading advanced CBCT images and integrating them with clinical data. This methodology ensures a comprehensive evaluation across three key axes:
Skeletal Axis: Assessing the relationship between the jaws and the condition of the joints, which is the foundation of advanced orthodontic treatment.
Dental Axis: Determining tooth position, the presence of any root diseases, or hidden decay.
Aesthetic Axis: Using 3D data to predict the outcome of treatment on the facial profile and the final smile.
Quality Protocols and Personal Supervision:
Being qualified from a prestigious international academic institution like the University of Parma, Italy, means that Dr. Mohamed Omara is committed to applying the most stringent European imaging and analysis protocols. This includes Quality Assurance protocols for the radiological device itself, which explains the center’s commitment to obtaining the International Quality Certificate (ISO). This personal supervision ensures that every radiological report issued is an integrated clinical analysis, and the approved treatment plan aligns with the highest international standards, making it one of the best centers in Egypt.

Section 10: Frequently Asked Questions about Dental Radiological Imaging (FAQ Section)
To cover the widest possible range of patient concerns and ensure comprehensiveness, here is an extended set of questions and answers:
Q: Are X-rays safe for pregnant women?
A: It is preferred to avoid dental X-rays during pregnancy as a precaution, except in cases of extreme emergencies that cannot be postponed. In such cases, they can be safely performed using a lead apron, and a consultation with the obstetrician should be sought first to ensure there are no contraindications.
Q: How often should routine X-rays be performed?
A: This depends on the patient’s health status and medical history. For healthy adults without active dental issues, the doctor may recommend routine panoramic X-rays every 3 to 5 years. Patients at high risk of decay or gum disease may need more frequent checkups every 6 to 18 months. CT scans are only performed when necessary for planning complex treatment (such as dental implants).
Q: Can decay be seen on Panoramic X-rays?
A: Yes, decay, especially deep decay, can be seen on panoramic X-rays. However, smaller intraoral X-rays (Periapical X-rays) or CT scans are more accurate in identifying small cavities or those located between teeth that are not visible to the naked eye.
Q: Do I need special preparation before a CT scan?
A: CBCT scans do not require any special preparation, apart from removing any jewelry or metallic objects in the head and neck area (such as earrings or removable dentures) that could obstruct image quality and cause artifacts.
Q: Do insurance companies cover the cost of panoramic and CBCT scans?
A: This heavily depends on the specific insurance policy. Most policies cover the cost of routine panoramic X-rays once every few years. CBCT scans are often covered if they are required as part of a major, medically approved treatment procedure, such as planning for dental implants or jaw surgery. You should consult your insurance company to determine coverage.
Q: Are X-rays safe for children?
A: Yes, X-rays are very safe for children and are necessary to monitor their dental growth and determine if there are extra teeth or impacted permanent teeth, which aids in early orthodontic planning. The lowest possible radiation dose is used, with strict application of lead aprons for protection.
Q: How long does the X-ray procedure take? And is it painful?
A: The imaging process is extremely fast and completely painless. Panoramic X-rays take less than a minute, including patient positioning. CBCT scans take only a few minutes (one or two minutes for the actual imaging) and require the patient to stand or sit still.
Q: How are digital X-ray images stored and transferred?
A: Images are stored digitally in the center using a secure medical image archiving system (PACS). They are often transferred to specialists and labs via the internet using high-quality digital files (DICOM), which makes it easy for specialized doctors (like Dr. Mohamed Omara) to access and analyze the images accurately without data loss.
Section 11: Egypt as a Leading Destination for Dental Medical Tourism: Advantages and Landmarks
In recent years, Egypt has emerged as a leading global destination not just for its historical sites, but also for the quality of its medical services, especially in dentistry. The concept of “Dental Medical Tourism” in Egypt has become an attractive option for patients from Europe, Arab countries, and Africa for multiple reasons:
Economic Advantage: The total cost of advanced treatment (such as complex dental implants requiring CBCT) in Egypt is significantly lower than the cost in North America or Europe, while maintaining the same international quality standards.
Quality and Expertise: The presence of internationally qualified medical staff, such as Dr. Mohamed Omara, who holds a Master’s degree from the University of Parma, Italy, ensures the application of the latest diagnostic and therapeutic protocols (such as relying on CBCT at every step).
Integrating Treatment with the Tourist Experience: Patients can complete their treatment (which sometimes requires scattered visits) and enjoy visiting the world’s most famous landmarks. The experience of receiving advanced dental care at a center, followed by a recovery period among the Pyramids of Giza, or the temples of Luxor and Aswan, is unmatched by any other medical tourism destination.
Ease of Access: Egypt’s central geographical location makes it easy and convenient to reach for many people.
Choosing a center committed to the highest standards of technological diagnosis, like Dr. Mohamed Omara Center, which ensures the use of CBCT in planning, gives the patient confidence that their decision to travel for treatment was sound and based on accuracy, not speculation.
Section 12: Conclusion and Future Outlook: Towards Error-Free Diagnosis
Integrating Panoramic and CBCT technologies into modern dental practice is a decisive factor in elevating the standard of healthcare. It enables doctors to move from the treatment phase to the phase of preemptive and accurate planning, minimizing surprises and risks.
To obtain the best possible diagnosis, one must always choose a center that combines advanced technology with deep clinical expertise. Ultimately, accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of every successful treatment. Therefore, Dr. Mohamed Omara Center is the trusted destination that guarantees its patients not only the latest imaging technologies but also the qualified expertise from prestigious European universities (Master’s from Italy) and personal supervision over every treatment step, making it one of the best centers in Egypt.
